Abstract:
Distributed Green computing which depends on Virtualization and Network. It is rapidly growing as an option in contrast to traditional office-based processing. Distributed computing turns out to be more far reaching, the vitality utilization of the system and processing Information and assets that support the cloud will raise. This is going on when there is raising consideration being paid to the need to orchestrate and oversee vitality use over the whole data and interchanges innovation (ICT) division.
Introduction:
While information house i.e. server farm vitality utilize has expected much consideration as of late, there has been less consideration paid to the vitality utilization of the transmission and exchanging systems are that are critical to associating clients to the cloud and transmission and additionally information handling and information stockpiling. I clarified that vitality utilization in transport and exchanging can be a huge level of aggregate vitality utilization in distributed computing. Distributed computing can empower more productive utilization of registering power, particularly when the processing undertakings are of low force or inconsistent. In any case, under a few conditions distributed computing can devour more vitality than unsurprising processing where every client plays out all figuring alone (PC).
Result and Discussion:
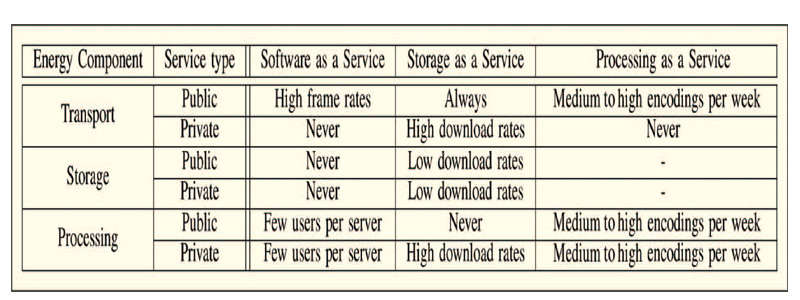
Fig: Different Conditions which Energy Consumption is significant
Conclusion: In this paper, I concluded a wide-ranging energy consumption analysis of cloud computing. The analysis process considered both public and private clouds they are two major clouds and included energy consumption in switching and broadcast as well as processing data and data storage. I have evaluated the energy consumption associated with three cloud computing services, namely storage as a service, software as a service, and processing as a service. Future services concerning about cloud computing is likely to include some combination of each of these service models & work flow. Power consumption in transport represents a significant proportion of total power consumption for cloud storage services at medium and high usage rates, public cloud storage can consume the order of 3-4 times more power than private cloud storage due to the increased energy consumption in transportation process. Nevertheless, public & private cloud storage services are more energy efficient than storage on local hard disk drives when files are only occasionally accessed. However, as the number of file downloads per hour increases, the energy consumption in transport grows and storage as a service consumes more power than storage on local hard disk drives. The energy savings from cloud storage are minimal. At reasonable and high screen refresh rates, power consumption in transport becomes significant and energy savings over midrange PCs are reduced and also optimizes the overall performance.
References:
- (2009). Cisco visual networking index: Forecast and methodology, 2009–2014.White paper.[Online]. Available: http://www.cisco.com.
- Weiss, BComputing in the clouds,[networker, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 16–25, 2007.
- Singh and P. K. Vara, BSmart metering the clouds,[ in Proc. IEEE Int. Workshops Enabling Techno. Infrastructures for Collaborative Enterprises, Groningen, The Netherlands, Jun.–Jul. 2009, pp. 66–71.
- Kondo, B. Javadi, P. Malecot, F. Cappello,and D. P. Anderson, BCost-benefit analysis of cloud computing versus desktop grids,[ in Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Parallel Distrib. Process., Rome, Italy, May 2009, DOI: 10.1109/IPDPS. 2009.5160911.